In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, revenue cycle management serves as the cornerstone of financial stability for healthcare organizations. At the heart of this intricate process lies the crucial function of medical billing. Accurate and efficient medical billing is vital for optimizing revenue, reducing claim denials, and ensuring the financial viability of healthcare providers. In this blog, we will explore the top 10 steps of medical billing in revenue cycle management, shedding light on the intricacies and challenges faced along the way. From patient registration to accounts receivable follow-up, each step plays a pivotal role in streamlining the billing process and maximizing revenue collection.
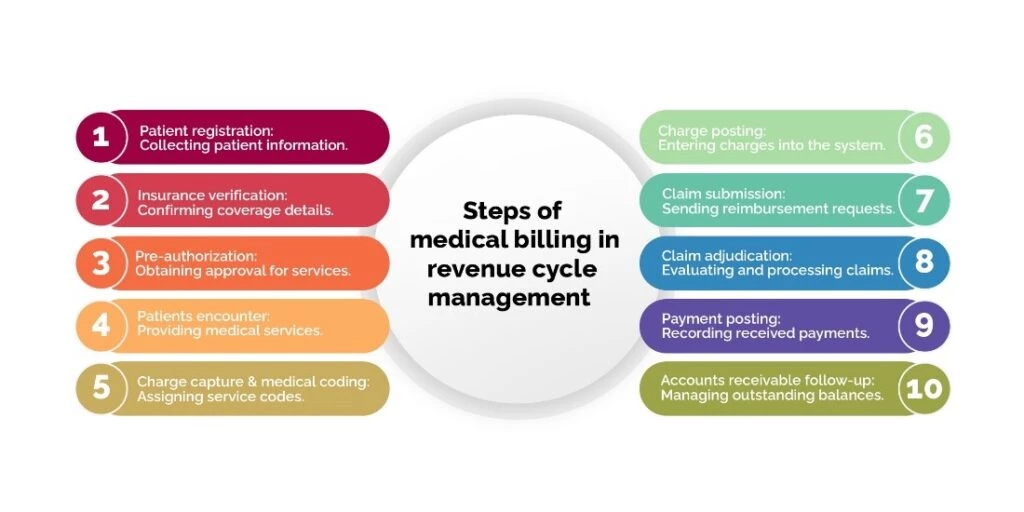
Steps of Medical Billing in Revenue Cycle Management
While each practice has its unique method for handling claims, basic procedures must be followed for medical billing process steps in RCM. When carried out methodically, these actions improve the efficiency of your revenue cycle.
1.) Patient Registration
Patient registration is the initial step in the revenue cycle management process. It involves collecting accurate and complete patient information, including demographic details, insurance coverage, and contact information. The challenges faced during patient registration include errors or omissions in data collection, which can lead to billing and reimbursement issues later in the process. To overcome these challenges, healthcare organizations can implement electronic registration systems that prompt for necessary information, use data validation techniques, and offer real-time verification of demographic and insurance details. Regular training for staff can also help ensure accurate data collection.
![]() Challenges – Gathering accurate and complete patient information can be challenging due to errors or omissions. This can lead to billing and reimbursement issues later in the process.
Challenges – Gathering accurate and complete patient information can be challenging due to errors or omissions. This can lead to billing and reimbursement issues later in the process.
![]() Solution –
Solution –
- Implement electronic registration systems that prompt for necessary information, use data validation techniques, and offer real-time verification of demographic and insurance details.
- Regular training for staff can also help ensure accurate data collection.
2.) Insurance Eligibility
Insurance eligibility verification is the second procedure in medical billing steps which includes confirming a patient’s insurance coverage and benefits before providing any medical services. The challenges in this step include the complexity of verifying insurance coverage, dealing with multiple insurance plans, varying coverage limitations, and changing policies. To address these challenges, healthcare organizations can utilize automated tools or electronic systems to streamline the insurance verification process. These tools can help access real-time information, verify eligibility, and determine coverage details accurately and efficiently.
![]() Challenges – Verifying insurance coverage can be time-consuming and complex, especially when dealing with multiple insurance plans, varying coverage limitations, and changing policies.
Challenges – Verifying insurance coverage can be time-consuming and complex, especially when dealing with multiple insurance plans, varying coverage limitations, and changing policies.
![]() Solution – Utilize automated tools or electronic systems to streamline the insurance verification process. This can help access real-time information, verify eligibility, and determine coverage details accurately and efficiently.
Solution – Utilize automated tools or electronic systems to streamline the insurance verification process. This can help access real-time information, verify eligibility, and determine coverage details accurately and efficiently.
3.) Pre-Authorization
Pre-authorization is the process of obtaining approval from insurance companies for certain procedures or services before they are performed. The challenges in this step include the time-consuming and burdensome nature of the process, as it requires detailed documentation and navigating through different payer requirements. To overcome these challenges, healthcare organizations can develop strong communication channels with payers to understand their pre-authorization requirements. Implementing electronic systems that automate pre-authorization requests and track the status of each request can also help reduce delays and improve efficiency.
![]() Challenges – Obtaining pre-authorization for certain procedures or services is essential to ensure reimbursement. However, the process can be burdensome, requiring detailed documentation and navigating through different payer requirements.
Challenges – Obtaining pre-authorization for certain procedures or services is essential to ensure reimbursement. However, the process can be burdensome, requiring detailed documentation and navigating through different payer requirements.
![]() Solution –
Solution –
- Develop strong communication channels with payers to understand their pre-authorization requirements.
- Implement electronic systems that automate pre-authorization requests and track the status of each request, reducing delays and improving efficiency.
4.) Patients Encounter
The patients encounter stage involves providing medical services to patients. Challenges in this step include providing quality care while accurately documenting the services rendered, especially in fast-paced healthcare environments. Incomplete or incorrect documentation can impact billing and reimbursement. To address these challenges, healthcare organizations can train healthcare providers on proper documentation practices and provide them with tools that facilitate accurate and timely capture of patient encounter details. Implementing electronic health record systems that prompt for necessary documentation elements and offer coding assistance can also help ensure accurate documentation.
![]() Challenges – Providing quality care while accurately documenting the services rendered can be a challenge, especially in fast-paced healthcare environments. Incomplete or incorrect documentation can impact billing and reimbursement.
Challenges – Providing quality care while accurately documenting the services rendered can be a challenge, especially in fast-paced healthcare environments. Incomplete or incorrect documentation can impact billing and reimbursement.
![]() Solution –
Solution –
- Train healthcare providers on proper documentation practices and provide them with tools that facilitate accurate and timely capture of patient encounter details.
- Implement electronic health record systems that prompt for necessary documentation elements and offer coding assistance.
5.) Charge Capture and Medical Coding
Charge capture and medical coding involve assigning appropriate service codes and ensuring accurate documentation for each procedure or service provided. Challenges in this step include coding errors, insufficient documentation, or a lack of coding knowledge, which can lead to claim denials or payment delays. To overcome these challenges, healthcare organizations can employ certified medical coders who are proficient in current coding guidelines. Regular audits and quality checks can be established to identify coding issues and provide feedback to coders. Open communication between coding staff and healthcare providers can also address any documentation gaps.
![]() Challenges – Assigning appropriate service codes and ensuring accurate documentation for each procedure or service is vital for accurate billing. However, coding errors, insufficient documentation, or lack of coding knowledge can lead to claim denials or payment delays.
Challenges – Assigning appropriate service codes and ensuring accurate documentation for each procedure or service is vital for accurate billing. However, coding errors, insufficient documentation, or lack of coding knowledge can lead to claim denials or payment delays.
![]() Solution –
Solution –
- Employ certified medical coders who are proficient in current coding guidelines.
- Establish regular audits and quality checks to identify coding issues and provide feedback to coders.
- Encourage open communication between coding staff and healthcare providers to address any documentation gaps.
6.) Charge Posting
Charge posting refers to the process of transferring charges from encounter forms or super bills into the billing system. Challenges in this step include data entry errors or missing charges, which can result in billing discrepancies and revenue loss. To address these challenges, healthcare organizations can utilize automated charge capture systems that integrate with electronic health record systems, reducing manual data entry. Robust reconciliation processes should also be implemented to identify and correct any discrepancies between encounter forms and the billing system.
![]() Challenges –
Challenges –
Transferring charges from encounter forms or super bills into the billing system can result in data entry errors or missing charges. This can lead to billing discrepancies and revenue loss.
![]() Solution –
Solution –
- Utilize automated charge capture systems that integrate with electronic health record systems, reducing manual data entry.
- Implement robust reconciliation processes to identify and correct any discrepancies between encounter forms and the billing system
7.) Claim Submission
Claim submission involves preparing and submitting claims accurately and timely to insurance payers for reimbursement. Challenges in this step include complex billing requirements, missing information, or formatting errors, which can result in claim rejections. To overcome these challenges, healthcare organizations can utilize practice management software that incorporates claim scrubbing features to identify errors before submission. Regular training for billing staff to stay updated on payer-specific requirements can also help improve claim accuracy. Implementing a robust quality assurance process to review claims before submission is also recommended.
![]() Challenges – Preparing and submitting claims accurately and timely is crucial to avoid claim rejections or denials. Complex billing requirements, missing information, or formatting errors can result in claim rejections.
Challenges – Preparing and submitting claims accurately and timely is crucial to avoid claim rejections or denials. Complex billing requirements, missing information, or formatting errors can result in claim rejections.
![]() Solution –
Solution –
- Utilize practice management software that incorporates claim scrubbing features to identify errors before submission.
- Regularly train billing staff to stay updated on payer-specific requirements and implement a robust quality assurance process to review claims before submission.
8.) Claim Adjudication
Claim adjudication is the process where insurance payers review and process the submitted claims. Challenges in this step include extensive scrutiny of claims, which can lead to delays or denials. Issues may include incomplete documentation, medical necessity questions, or discrepancies between coding and billing. To address these challenges, healthcare organizations should develop strong relationships with payers, establish clear lines of communication, and promptly address any requests for additional information. Monitoring claim status regularly and following up on any delayed or denied claims is crucial. An effective appeals process should be established to challenge claim denials when appropriate.
![]() Challenges – Claims can undergo extensive scrutiny during the adjudication process, leading to delays or denials. Issues may include incomplete documentation, medical necessity questions, or discrepancies between coding and billing.
Challenges – Claims can undergo extensive scrutiny during the adjudication process, leading to delays or denials. Issues may include incomplete documentation, medical necessity questions, or discrepancies between coding and billing.
![]() Solution –
Solution –
- Develop strong relationships with payers, establish clear lines of communication, and promptly address any requests for additional information.
- Monitor claim status regularly and follow up on any delayed or denied claims promptly.
- Establish an effective appeals process to challenge claim denials when appropriate.
9.) Payment Posting
Payment posting involves accurately recording received payments and posting them to the appropriate patient accounts. Challenges in this step include manual processes, data entry errors, and reconciliation challenges, which can result in payment posting delays or inaccuracies. To overcome these challenges, healthcare organizations should automate payment posting processes using electronic remittance advice (ERA) and electronic funds transfer (EFT) systems. Implementing robust reconciliation procedures to identify and resolve any discrepancies between payment records and expected reimbursement is essential.
![]() Challenges – Accurate and timely recording of received payments and posting them to the appropriate patient accounts is essential for proper financial management. However, manual processes, data entry errors, and reconciliation challenges can result in payment posting delays or inaccuracies.
Challenges – Accurate and timely recording of received payments and posting them to the appropriate patient accounts is essential for proper financial management. However, manual processes, data entry errors, and reconciliation challenges can result in payment posting delays or inaccuracies.
![]() Solution –
Solution –
- Automate payment posting processes using electronic remittance advice (ERA) and electronic funds transfer (EFT) systems.
- Implement robust reconciliation procedures to identify and resolve any discrepancies between payment records and expected reimbursement.
10.) Accounts Receivable Follow-Up
Accounts receivable follow-up involves managing outstanding balances and ensuring timely payment from patients or insurance companies. Challenges in this step include lack of communication, delayed responses, or disputes that can prolong the accounts receivable cycle. To address these challenges, healthcare organizations should implement proactive accounts receivable management strategies. This includes regular follow-up with patients and payers to address any outstanding balances or claim issues. Utilizing automated reminders and escalation processes can ensure timely resolution of payment disputes or outstanding claims.
Challenges
Managing outstanding balances and ensuring timely payment from patients or insurance companies can be challenging. Lack of communication, delayed responses, or disputes can prolong the accounts receivable cycle.
Solution
Implement proactive accounts receivable management strategies, including regular follow-up with patients and payers to address any outstanding balances or claim issues.
Use automated reminders and escalation processes to ensure timely resolution of payment disputes or outstanding claims.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of medical billing is a complex task, but by understanding and implementing the top 10 steps of medical billing in revenue cycle management, healthcare organizations can achieve financial success and operational excellence. Collaborating with a reputable RCM company that specializes in medical coding, claim submission, and revenue optimization can provide invaluable support and expertise throughout the billing process. Together, healthcare providers and RCM companies can streamline operations, enhance revenue collection, and ensure accurate reimbursement, ultimately empowering healthcare organizations to focus on what matters most: delivering exceptional patient care.
Reference:
• American Academy of Professional Coders (AAPC)
• Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA)
• Medical Group Management Association (MGMA)







